Polyphenols are the undercover superheroes of extra virgin olive oil, delivering not only vibrant flavors but also impressive health benefits. If you’ve ever wondered what makes high-quality olive oil so much better for you than the generic stuff sitting on a supermarket shelf, the answer lies in these powerful natural compounds. Known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, polyphenols play a central role in promoting health and well-being.
At Wildly Virgin, we believe olive oil is more than a pantry staple—it’s a gateway to flavor, wellness, and the magic of tradition. Let’s dive into everything you need to know about these mighty molecules and how they elevate both your cooking and your health.
What Exactly are Polyphenols?
Polyphenols are naturally occurring compounds found in plants, fruits, and vegetables. They are what give plants their color and help protect them from environmental stressors. Scientists have identified over 8,000 types of polyphenols, also known as biophenols, each with unique properties and potential health benefits.
In extra virgin olive oil, the most significant polyphenols include:
Hydroxytyrosol: One of the most potent antioxidants found in olive oil, known for its exceptional free radical-fighting abilities
Oleuropein: Responsible for the characteristic pungent, peppery sensation in fresh olive oil and praised for its anti-inflammatory properties
Tyrosol: Another powerful antioxidant that works synergistically with hydroxytyrosol
Oleocanthal: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties similar to ibuprofen
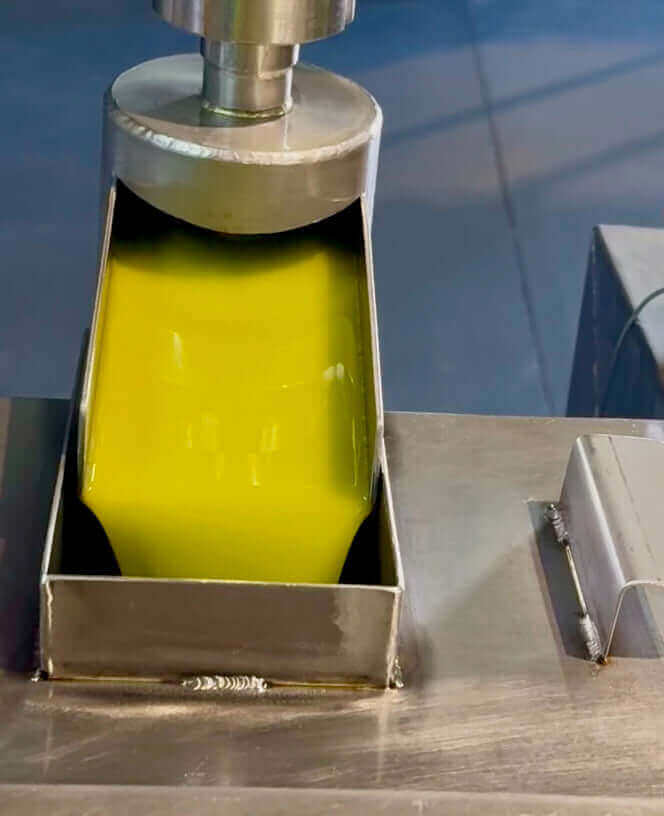
These compounds serve multiple purposes in olive oil. They create the complex flavors we associate with high-quality extra virgin olive oil - from bitter to pungent notes. More importantly, they act as natural preservatives, helping the oil resist oxidation and maintain its quality over time. This is why high-polyphenol olive oils typically have a longer shelf life and better stability than their lower-quality counterparts.
The Health Benefits of Polyphenols
The health benefits of polyphenols have been confirmed by numerous studies (see our deep dive on the health benefits of EVOO), but decades after scientists have been studying them, we still don’t know exactly how they work. Despite the mystery, here are the some of most well-researched benefits of polyphenols:
Antioxidant Properties: Polyphenols fight harmful free radicals, helping protect your body from damage linked to aging and chronic diseases.
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Regular consumption of polyphenol-rich foods, like extra virgin olive oil, has been linked to lower levels of inflammation, which can reduce the risk of heart disease, arthritis, and other chronic conditions.
Heart Health: Polyphenols can help lower LDL cholesterol (the “bad” kind) and improve overall vascular function, contributing to a healthier cardiovascular system.
Brain Health: Emerging research suggests that polyphenols may protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, boosting cognitive function and memory.
Longevity: In Mediterranean cultures, where olive oil is a dietary staple, polyphenols are believed to play a role in increased life expectancy and overall wellness.
sources: International Journal of Molecular Sciences, Nutrition Reviews, European Journal of Nutrition
How to Choose High-Polyphenol Olive Oil
When shopping for olive oil rich in polyphenols, focus on these key factors:
Early Harvest: Choose oils made from olives picked before full ripeness, which contain significantly higher polyphenol levels.
Single Farm, processed on site: Time is the enemy of polyphenols, so farms that produce their own olive oil and process on site typically have the fasted milling times and higher polyphenol outputs.
Freshness: Look for oils harvested within the past year.
Proper Packaging: Select oils in dark bottles that protect polyphenols from light and heat degradation.
Quality Indicators: Lower acidity levels (below 0.3%) often indicate fresher, higher-quality oil with better polyphenol content.
Learn more about how to select the best quality olive oil in our Wildly Virgin Guide to Quality and Authenticity.
Using Olive Oil Rich in Polyphenols
To maximize the benefits of polyphenol-rich olive oil, consider these practices:
Cold Applications: Use it as a finishing oil on salads, drizzle over cooked vegetables, or add to dips and spreads. This preserves the polyphenols while enhancing flavor.
Low-Heat Cooking: While high heat can diminish polyphenol levels, gentle warming (up to 180°C/350°F) is totally fine. Use it for light sautéing or low-temperature roasting.
Storage: Keep your olive oil in a cool, dark place to preserve its polyphenol content and overall quality.
Discover the difference that high-polyphenol, small-batch extra virgin olive oil can make in your cooking and health. Wildly Virgin's Portuguese olive oils are crafted with high polyphenols through early harvesting and careful processing. Try our polyphenol full Portuguese olive oils today.